ISTA作为宝马维修车间系统,供全世界经销商机构中使用的BMW Group车辆诊断和编程应用使用。近日获取到了安装程序与对应的数据库,故对其进行了相应的探究。
作为经销商使用的软件,宝马为该程序添加了许可证校验无可厚非。但是它在互联网流传过程中,不但其本体获取存在一定的困难,其许可证的获取也颇有意思,与我们通常能够看到的破解软件有着一定的区别。
程序安装前总计约23.1GB,完成安装后总计约124GB,蔚为壮观,主要由对应的数据库文件所组成。
完成安装后打开程序,第一屏就能看到提示许可证失效,需要进行激活。点击两次下一步后就能看到输入具体激活码的页面。随便输入一些字符,显然是无效的,下一步按钮始终为灰色。
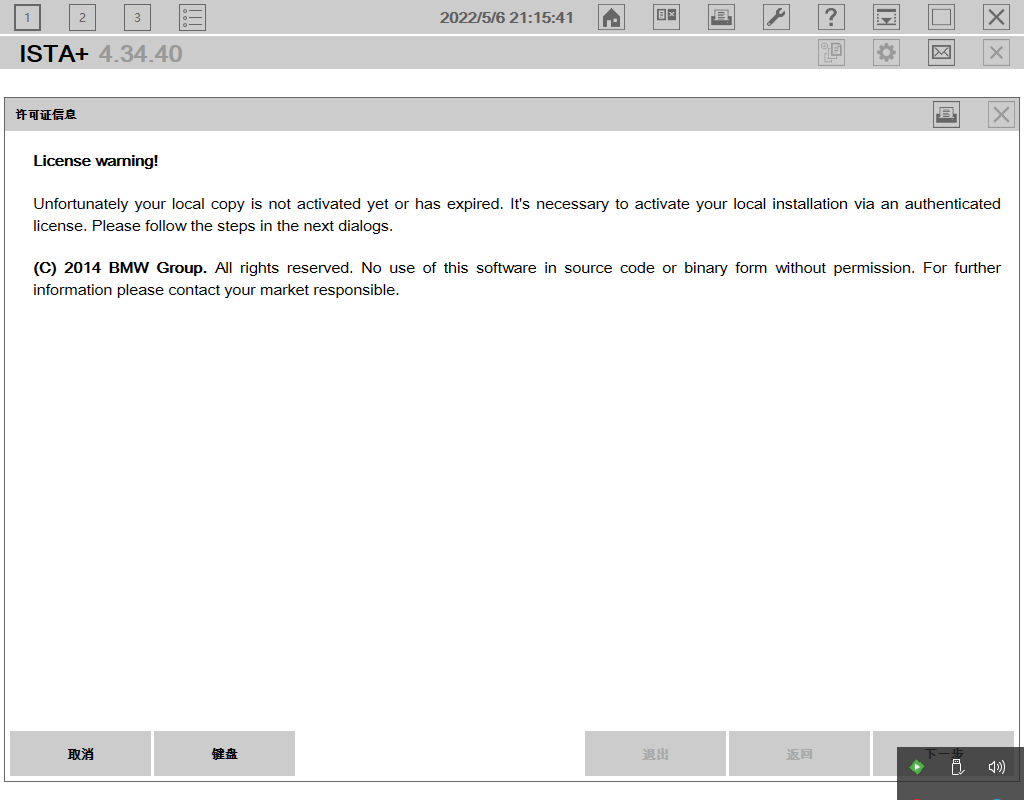
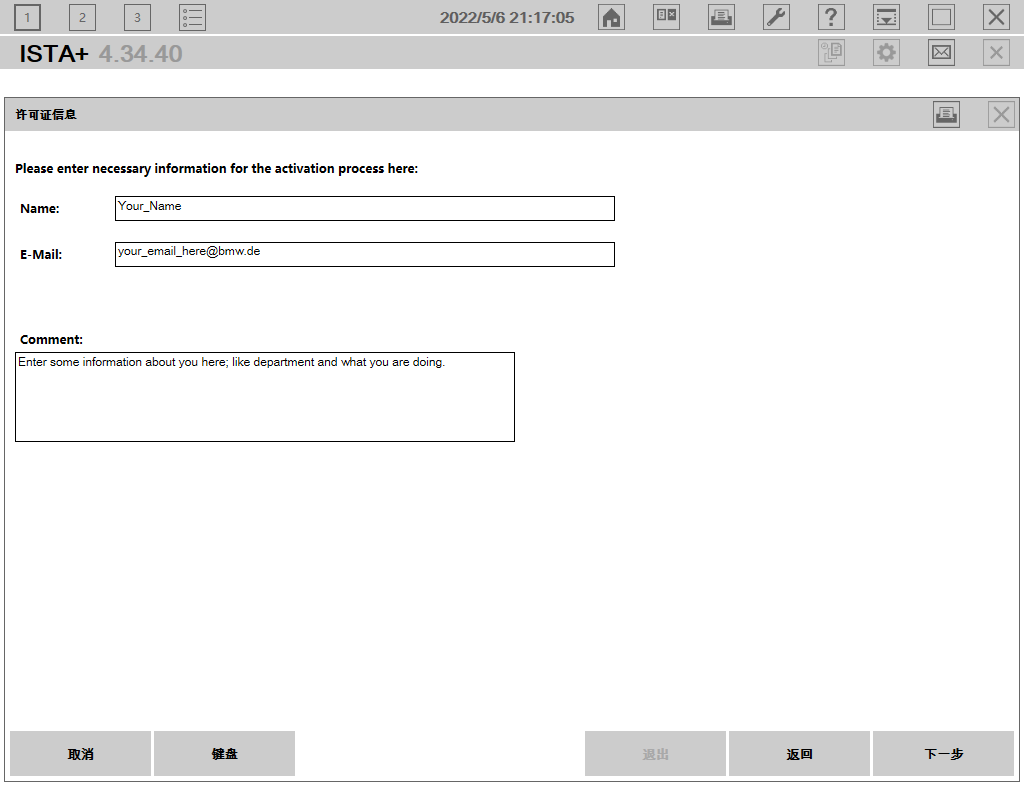
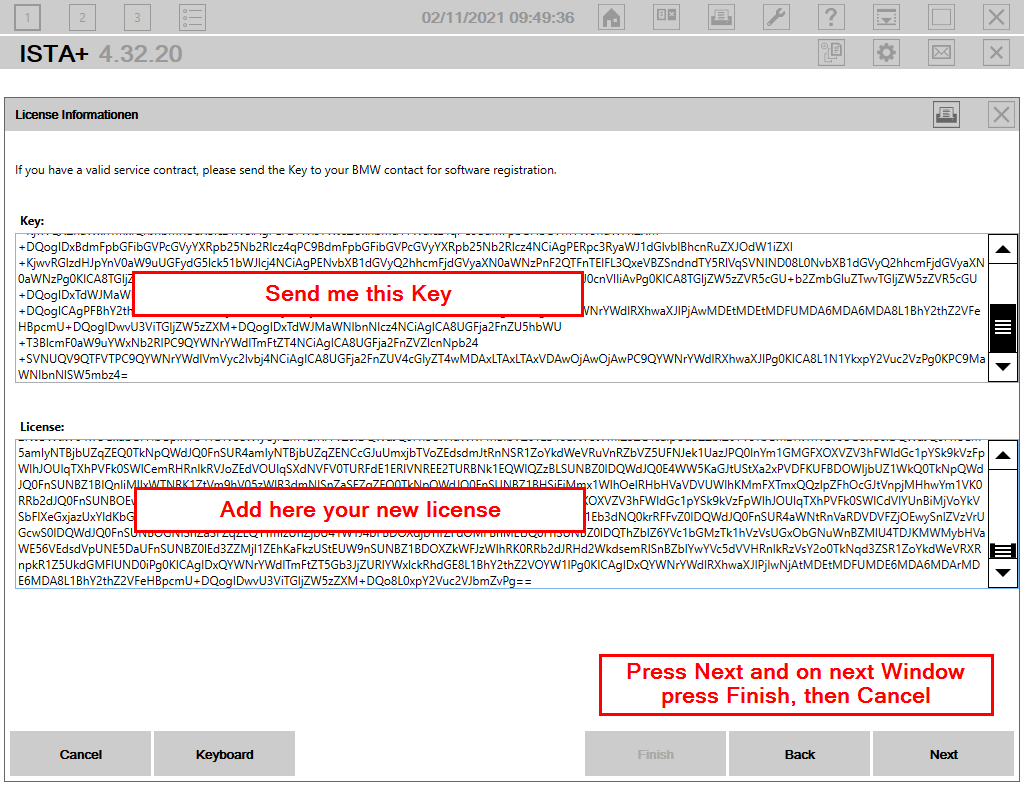
程序本身,不论是从哪里找到下载也好,还是从什么论坛购买也好,这都是很正常的情况。但是到这个具体激活的地方,不论是国内论坛还是国外论坛,都可以见到一种,你执行到这一步,获取到key,将这个key通过私信发给某个人,由他将对应的license发给你的操作流程。
而这一步,是免费的。这里,就是有意思的地方了。似乎是有人掌握了keygen但是并没有将其与软件一并公开,虽然不公开,也没有借此进行盈利,着实有点没有理解其背后具体的原因。同时有的版本其主程序甚至使用safengine shielden进行了加壳。并对签名校验部分的公钥进行了调换。属实有趣。
扯远了,还是回归主题,那么从程序主入口入手,稍作检查,GUI部分是使用.NETFramework 4.8编写的,那就好办了,代码的查看、编辑等都会方便很多。
以下内容均以版本4.34.40.26161为基础,当前已经完成在4.41.41.25274原版程序上的验证,整体思路没有问题。
原版MSI安装存在对环境与调用方的校验,无法直接安装。可以使用
SuperOrca对表InstallExecuteSequence中LauncherNotFound与NotCalledByLauncher两个Action进行删除即可正常安装,完成安装后注意调整程序配置即可。
从程序入口出发,使用dnSpy打开程序ISTAGUI.exe,检查程序组成,原则上,是宁可错杀不可放过,对于相关的校验逻辑,都进行对应的处理。
稍作检查,能发现,程序使用dotfuscator进行了较为轻度的混淆,主要是部分逻辑流程的打乱和字符串的不可直接识读。使用de4dot可较为方便得除去相关混淆逻辑。(这个并不是宝马的限制,这个是Sedoy对其发布版本进行的保护措施)
完整性校验
很快,类型BMW.Rheingold.SecurityAndLicense.IntegrityManager引起了注意,其构造函数是校验程序完整性的代码,对其稍作整理,可得如下代码,为便于理解,移除部份不重要代码并稍作调整。。
class IntegrityManager
{
private readonly string pk_xml = "<RSAKeyValue><Modulus>████████████████</Modulus><Exponent>████</Exponent></RSAKeyValue>";
internal IntegrityManager()
{
const string filePath = "..\\..\\..\\Ecu\\enc_cne_1.prg";
const string sigPath = "..\\..\\..\\Ecu\\sig_gis_1.prg";
const string directoryName = "TesterGUI";
const string searchPattern = "*.dll,*.exe";
VerifyData(filePath, sigPath);
var encryptedHashFiles = DecryptFile(filePath, _password, _salt, _iterations);
var source = from s in Directory.EnumerateFiles(Environment.CurrentDirectory, "*.*", SearchOption.TopDirectoryOnly)
where searchPattern.Contains(Path.GetExtension(s).ToLower())
select s;
var istaHashFilesToCheck = (from path in source select new HashFileInfo(path, directoryName)).ToList();
foreach (var istaHashFile in istaHashFilesToCheck)
{
var hashFileInfo = encryptedHashFiles.FirstOrDefault(item => item.FileName.Equals(istaHashFile.FileName));
if (hashFileInfo != null && hashFileInfo.Hash != istaHashFile.Hash)
{
Environment.Exit(0);
}
}
}
private void VerifyData(string fileToVerify, string signaturePath)
{
using var rsacryptoServiceProvider = new RSACryptoServiceProvider();
var buffer = File.ReadAllBytes(fileToVerify);
var signature = File.ReadAllBytes(signaturePath);
rsacryptoServiceProvider.FromXmlString(pk_xml);
new SHA512Managed().ComputeHash(signature);
if (!rsacryptoServiceProvider.VerifyData(buffer, CryptoConfig.MapNameToOID("SHA1"), signature))
{
Environment.Exit(1);
}
rsacryptoServiceProvider.PersistKeyInCsp = false;
}
}
该部分代码,主要包含两个步骤:
- 通过校验对应的
RSA签名,以校验enc_cne_1.prg是否篡改,供进一步校验使用。 - 通过读取
enc_cne_1.prg获取需要校验的文件,逐个计算SHA256值以校验文件是否被篡改。
上述中任意一步的校验不一致,均将导致程序退出,使程序无法使用,那么显然,本次修改所涉及的最大范围,限于此列表。
考虑到程序端不存在RSA私钥,使用RSA公钥来校验完整性,看似安全,但是,通过自行生成一对密钥对文件重新进行签名。这样一来,就能够更新上述列表中任意文件而不会触发起校验的异常。
以上方法属于顺着程序本身的思路来的。实际操作上,直接将这段代码移除,就会使校验不通过导致程序退出这个情况彻底不存在。
PS: 此处有一个暗坑,enc_cne_1.prg中的文件列表,不包含IstaOperation.exe,如果以其其中的列表作为执行补丁的范围,则会导致该文件被漏掉,然而该程序中,却是包含IntegrityManager的,从而导致整个程序的部分功能,没法正常执行。
那么还有哪里有程序完整性的校验阻碍修改程序呢,进行对应的调试与查找,BMW.Rheingold.CoreFramework.WcfCommon.IstaProcessStarter下的中也存在相关的代码CheckSignature,对其稍作整理,代码如下。
private static void CheckSignature(string pathToIstaProcessFile)
{
Assembly executingAssembly = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly();
if (!Assembly.ReflectionOnlyLoadFrom(pathToIstaProcessFile).GetName().GetPublicKeyToken().SequenceEqual(executingAssembly.GetName().GetPublicKeyToken())) {
throw new InvalidOperationException();
}
}
在启动其他子程序之前,会通过校验当前程序的publickey与子程序的publickey是否一致,来校验程序的完整性。
那么显然的,只要不校验,就不存在这个问题了。
校验请求生成
在处理具体许可证生成前,可以先看一眼,程序的key是怎么生成的,可以在BMW.Rheingold.CoreFramework.LicenseManagement.LicenseWizardHelper处,找到CalculateLicenseRequest方法。没有什么特殊的,就是生成机器特征码,收集一些其他信息,生成xml并转换为base64编码。
也可以根据这个思路顺下去,自己签发license,那就和通常网上常见的模式一样了。
许可证校验
一旦程序已经失去了完整性校验,那么程序对于许可证的校验也就完全失去了把控。
通过检索,可以找到namespace BMW.Rheingold.CoreFramework.LicenseManagement 下的LicenseStatusChecker,对其稍作整理,可得如下代码,为便于理解,移除部份不重要代码并稍作调整。
public class LicenseStatusChecker
{
internal LicenseStatus IsLicenseValid(LicenseInfo licenseInfo, bool isid)
{
this.GetComputerCharacteristics(isid, licenseInfo);
var licenseKey = licenseInfo.LicenseKey;
licenseInfo.LicenseKey = new byte[0];
var hash = this.GetHashValueFrom(licenseInfo);
if (!this.GetRSAPKCS1SignatureDeformatter().VerifySignature(hash, licenseKey))
{
return LicenseStatus.INVALID;
}
if (checkHypervisor())
{
return license.SubLicenses.Any(license => license.PackageName == "SyntheticEnv") ? LicenseStatus.VALID : LicenseStatus.INVALID;
}
if (licenseInfo.Expiration > DateTime.Now)
{
return LicenseStatus.VALID;
}
return LicenseStatus.EXPIRED;
}
private byte[] GetHashValueFrom(LicenseInfo licInfo)
{
using var memoryStream = new MemoryStream();
new XmlSerializer(typeof(LicenseInfo)).Serialize(memoryStream, licInfo);
return SHA1.HashData(memoryStream.GetBuffer());
}
private RSAPKCS1SignatureDeformatter GetRSAPKCS1SignatureDeformatter()
{
RSACryptoServiceProvider key = new RSACryptoServiceProvider();
key.ImportParameters(new RSAParameters()
{
Modulus = Convert.FromBase64String("████████████████"),
Exponent = Convert.FromBase64String("████")
});
RSAPKCS1SignatureDeformatter signatureDeformatter = new RSAPKCS1SignatureDeformatter((AsymmetricAlgorithm) key);
signatureDeformatter.SetHashAlgorithm("SHA1");
return signatureDeformatter;
}
}
内容也很有意思,可以发现,换标Z4的丰田的Supra,也是使用这套程序进行车辆诊断,但是使用的是另一套激活码,两者并不通用。其程序本体两者也并不通用,破解方式也有所区别,暂时还未具体研究,这里不作展开了。
可以发现,首先,它对收到的LicenseInfo序列化求SHA-1(不包含licenseKey),同时提取出其中的licenseKey,然后用程序预置的公钥初始化RSAPKCS1SignatureDeformatter验证签名是否有效。所以另一种思路就更加直接了,只要我直接把你这个密钥对给替换了,并实现一下签名的操作,那我自己就能给license request签名给签上了,就不需要各种道高一尺魔高一丈的操作了,实现其实类似,主要的问题还是在如何通过程序化的方法将修改il的操作自动化。
显然,简单地将IsLicenseValid的返回值,修改为LicenseStatus.VALID,就不再存在校验这个操作了。
但是,仅对以上部分进行修改,看似系统已经能够正常使用了,但是选择完车辆信息后,仍然无法查看维护信息,进步检索发现类型BMW.Rheingold.CoreFramework.LicenseManager中的VerifyLicense函数,也是大同小异,分门别类地进行了校验,或者比如不允许系统时间早于程序编译时间等等。
以上就是系统能够正常查看维护手册所需要进行的补丁内容。
为了使程序能够正常对车辆完成诊断,程序还会通过PsdzServiceImpl.dll与另一个使用java编写的PSdZ模块进行交互,而交互的过程中,会抛出一组参数不能同时为空的异常,经过查找相关代码如下:
private static String generateOrganizationId(int dealerId, int plantId) {
String organizationId;
if (dealerId == 0) {
if (plantId == 0) {
throw new PSdZArgumentException(PSdZErrorCodes.DEALER_ID_AND_PLANT_ID_MUST_NOT_BOTH_BE_0);
}
organizationId = Integer.toString(plantId, 16);
} else if (plantId != 0) {
throw new PSdZArgumentException(PSdZErrorCodes.EXACTLY_ONE_OF_DEALER_ID_AND_PLANT_ID_MUST_BE_0);
} else {
organizationId = Integer.toString(dealerId, 16);
}
return organizationId;
}
所以,除了激活的校验以外,还需要定位到调用PsdzServiceImpl.dll时,传入的参数对应的函数,将其修改为非零值,这样就能够正常进行诊断了。
完成激活
对相应文件进行替换之后,理论上启动时无需输入相关信息,可直接进入。
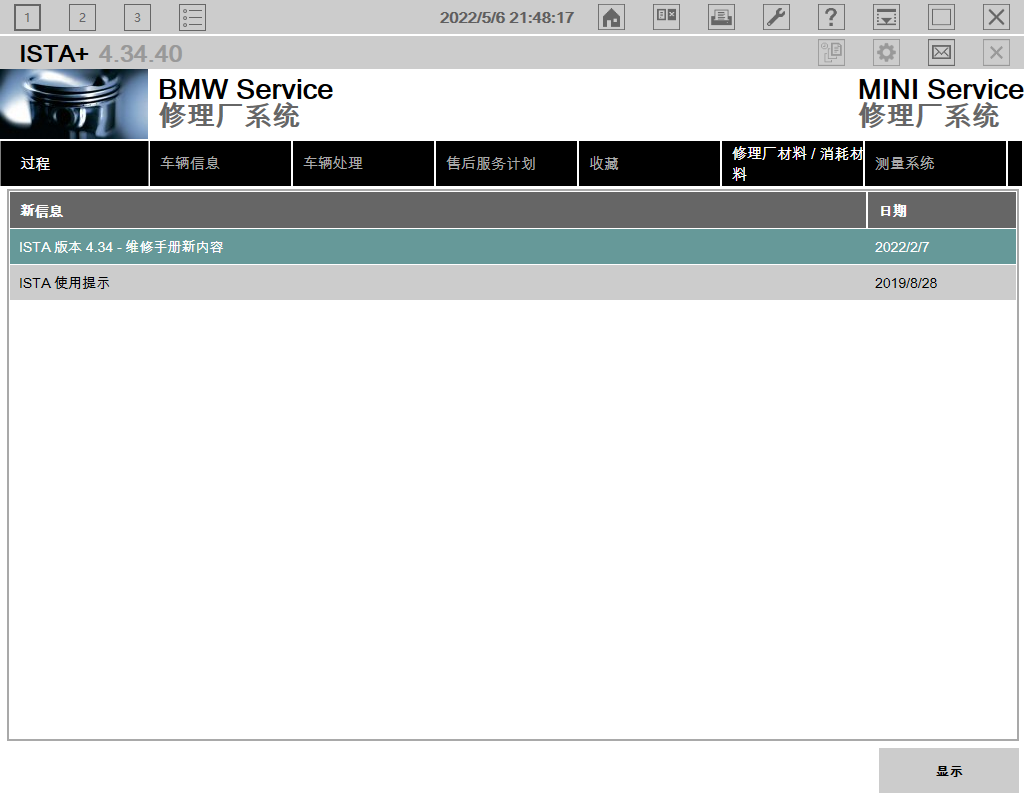
但是在使用过程中,日志里还是能看到许多提示激活失败的记录,查看无大碍,部份功能受影响,经排查,可以在注册表或者配置文件增加一个证书,确保程序在一些情况下,能正常读取到一个非空的证书信息,以减少这类报错。
当然,也可以通过在ISTAGUI.exe.config的appSettings下增加License键值对,注意字符串转义。
根据issue的反馈,应该是能过正常使用没问题了的。可一个没注意,使用该补丁的【免许可证】2022年12月下旬诊断维修指南编程瑞金 Rheingold(ISTA-D)4.39.20绿色版已经开始传播,甚至不清楚是具体哪位用具体哪个版本的ista-patcher制作并传播的,连个署名都没有,着实是不大好。
相关链接
- 基于本文实现的ISTA-Patcher
- 上文提到的需要添加的注册表文件